CORPORATE SUSTAINABILITY RESPONSIBILITY
企業永續責任
Supply Chain Management
供應鏈管理
HDRE Supplier Code of Conduct
HDRE Supplier Code of Conduct
HDRE is committed to social responsibility, environmental protection, business ethics, and sound corporate governance. We expect all suppliers to uphold the same standards, ensuring a supply chain that is safe, transparent, and sustainable.
Suppliers must comply with this Code as well as the laws and regulations in their operating locations—including, but not limited to, Taiwan’s Labor Standards Act, Occupational Safety and Health Act, Environmental Basic Act, and Personal Data Protection Act.
Suppliers are also expected to safeguard human rights, fulfill environmental responsibilities, and uphold integrity in business practices.
HDRE encourages suppliers to extend these requirements to their downstream suppliers, contractors, and partners. Supplier adherence to this Code will be considered in HDRE’s procurement decisions. Through collaboration, communication, audits, and ongoing evaluations, we aim to drive continuous improvement across the supply chain.
In cases of severe violations of this Code, HDRE reserves the right to suspend or terminate the business relationship.
This Code is established with reference to the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) Code of Conduct, the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, the ILO Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work, and the UN Universal Declaration of Human Rights, among other international standards.
The Code is organized into six key categories: Labor & Human Rights, Health & Safety, Environmental Protection, Ethical Conduct, Management Systems, and Social Participation.
Full details are available in the HDRE Supplier Code of Conduct (2025.09) .pdf
Supplier Management
HDRE has established a comprehensive supplier management framework that follows a “quality first, cost second” approach. Under this principle, specifications and quality requirements must be met through QA review, while sustainability performance is incorporated as a core evaluation criterion. This framework covers new supplier screening, ongoing management of existing suppliers, and a tier-based improvement mechanism.
- Vendor Screening and Management Proces
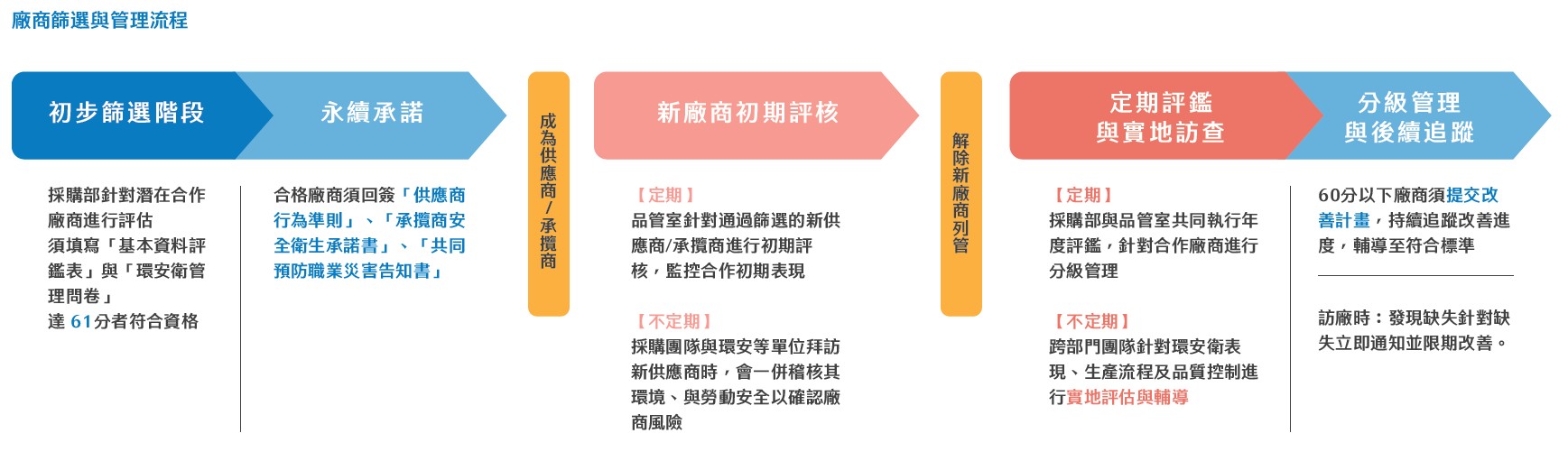
- New Supplier Screening: Evaluation Criteria and Sustainability Requirements
|
Assessment Dimensions |
Basic corporate qualifications (10%), product and technical capability (60%), and sustainability performance (30%). |
|
Required Documents |
Supplier Basic Information Assessment Form and Supplier EHS Management Questionnaire. |
|
Passing Criteria |
A minimum total score of 61 points is required. |
|
Sustainability Commitments |
Qualified suppliers must sign the Supplier Code of Conduct, the Contractor Safety and Health Commitment, and the Joint Occupational Hazard Prevention Notice. |
|
2024 Screening Results |
Number of new suppliers screened: All passed. |
- Supply Chain Impact Assessment and Management
HDRE has established a systematic framework for assessing environmental and social impacts across its supply chain.
On the environmental front, supplier performance is evaluated through EHS questionnaires and on-site visits to obtain a comprehensive understanding of environmental management practices.
According to the 2024 assessment results, no suppliers demonstrated any significant negative environmental impacts. HDRE continues to monitor key issues such as waste management and energy efficiency.
On the social front, the assessment focuses on occupational health and safety, labor rights, and workplace conditions. Through coordination meetings, job hazard analyses, and related mechanisms, HDRE ensures that suppliers meet its social responsibility requirements, with all suppliers actively cooperating with recommended improvements.
- EHS Questionnaire Tiered Management
To effectively manage supplier sustainability performance, HDRE has implemented a three-tier management system. Suppliers are classified as A, B, or C based on their EHS questionnaire scores, with differentiated management strategies applied to each tier.
The 2024 assessment results indicate strong overall performance, with no suppliers classified as Tier C.
Supplier Audits
- Supply Chain Integrated Management Enhancement Measures
| Vendor Types | Monitoring Mechanisms | Quality Control Outcomes | Safety and Health Management Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Suppliers |
Factory Acceptance Testing (FAT) |
HDRE conducts pre-shipment inspections for materials and equipment to confirm that technical specifications and quality standards are met. |
HDRE conducts safety testing for special materials to ensure they contain no harmful substances. Suppliers are required to provide Safety Data Sheets (SDS). |
| On-Site Supplier Audits |
On-site supplier assessments are carried out by a cross-functional team from Procurement, EHS, and QA. The team reviews production processes, quality control systems, and environmental practices. In 2024, 18 supplier site visits were completed. |
On-site assessments are carried out to review supplier workplace safety and occupational health systems, with attention to high-risk processes. |
|
| Contractors |
Corrective Action Management |
Corrective action requests are issued for materials that do not meet specifications. |
Special management measures are applied to materials with potential safety risks, including hazardous-goods storage rules and transport safety requirements, ensuring safe handling from supply to use. |
| Project Site Inspections |
Unscheduled quality checks are conducted at project sites to monitor construction quality and progress and to resolve issues promptly. |
Site safety facilities and protective measures are inspected to confirm control of hazardous work and compliance with environmental protection practices. |
|
| Quality Assurance Oversight |
Quality deviation notices are issued for construction-related issues. |
A complete construction safety management system is in place, including PPE requirements, permits for high-risk work, and equipment safety checks, ensuring safe operations for all contractors. |
|
| Safety and Risk Control |
Contractor construction safety and quality plans are reviewed to ensure self-inspection and segment-based checks are carried out. |
In 2024, 100% of contractors signed safety commitment forms and completed Job Hazard Analyses (JHA). |
Three Key Future Goals for Supply Chain Management
1. Strengthening the Quality Monitoring System
HDRE will continue to enhance its supply chain quality monitoring framework.
The company plans to expand site inspection coverage and reinforce material and equipment inspection mechanisms to ensure high-quality performance at every stage.
ISO 9001 quality management will be extended to subsidiaries, alongside the planned 2025 quality system certification for the Shide Factory, aiming to establish unified group-wide quality standards.
HDRE will also optimize construction specifications and develop tailored standard operating procedures for different project types.
2. Advancing a Health and Safety–Focused Supply Chain
Health and safety will remain a major driver of HDRE’s sustainability development.
The company will strengthen on-site supplier guidance, with stricter evaluation criteria for key suppliers such as those involved in waste management and environmental services.
A proactive performance management framework will be established to improve EHS evaluation processes.
HDRE will also participate in programs such as the government’s “Healthy Workforce Sustainability Leadership Initiative” to enhance overall occupational safety and health practices.
3.Enabling a Net-Zero Supply Chain
HDRE will lead its supply chain toward shared carbon-neutral goals in response to global net-zero trends.
The company will deepen green procurement practices, prioritizing suppliers with environmental certifications and encouraging the use of renewable energy and low-carbon technologies.
A supplier carbon-footprint tracking mechanism will be developed to support partners in setting reduction plans, contributing to climate action while achieving balanced economic and environmental outcomes.